
Home | Levels | CQS | Rating | FAQ | Papers | Code | Blog | Calc (v3.Eng.Generic) | Calc (v3.Eng.FPS) |
CQS is the ConsScale Quantitative Score.
In addition to the qualitative measure provided by ConsScale in the form of the 13 conceptual levels
of consciousness, a related quantitative score (the CQS) can be also calculated.
See below for specific information about the CQS and how it is calculated.
CQS possible values range from 0 to 1000.
See Table 1 for main CQS reference values.
See Figure 1 for a graphical representation of CQS values.
See Calculating the CQS for an explanation of how CQS is calculated.
See Video CQS for a brief presentation about CQS.
| LEVEL | DESCRIPTION | CQS | |
| 1 | Decontrolled | 0.00 | |
| 2 | Reactive | 0.18 | |
| 3 | Adaptive | 2.22 | |
| 4 | Attentional | 12.21 | |
| 5 | Executive | 41.23 | |
| 6 | Emotional | 101.08 | |
| 7 | Self-Conscious | 200.03 | |
| 8 | Empathic | 341.45 | |
| 9 | Social | 524.54 | |
| 10 | Human-Like | 745.74 | |
| 11 | Super-Conscious | 1000.00 |
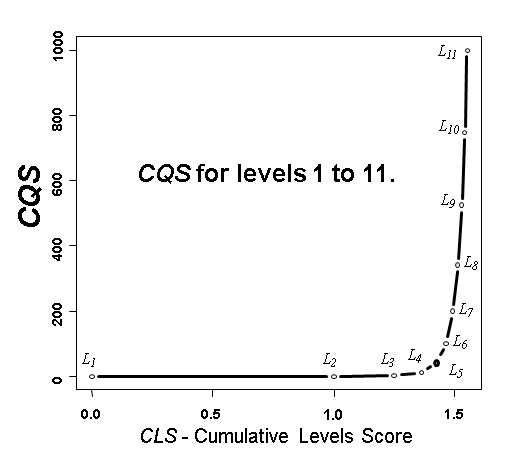
FIGURE 1. CQS values for agents qualifying for levels 1 to 11.
|
|
X-axis represents the CLS value, and Y-axis the resulting CQS.
CLS is the ConsScale Cumulative Score. See below. |
|
The CQS curve depicted in Fig. 1 spans from 0 to 1000 in an exponential fashion, representing the cumulative synergy produced by the addition and integration of cognitive features level after level. As the perceived overall cognitive performance increases, the score also increases exponentially, providing significant values from levels 4 and 5 upwards (see Table 1). |
CALCULATING THE CQS. The ConsScale Quantitative Score.
|
First of all, remember that you don't need to calculate the CQS yourself, you can use the online ConsScale Calculator. Having a quantitative score associated with the scale is a benefit from the following points of view: on one hand, as implementations can be evaluated concretely, individual and comparative studies are possible; on the other, specific fitness functions could be defined in order to apply evolutionary computing approaches. The CQS is designed to cover all the possibilities that could exist in a MC implementation, i.e. all possible combinations of CSi,j. the CQS is able to provide a specific numerical value for each conceptual level; additionally, non-canonical implementations which do not comply exactly with a concrete level (because they also show a partial amount of features from other levels) can be quantitatively evaluated and assigned a value between two canonical levels (see Figure 1). Doing the maths: The CQS can be calculated in three steps. First of all, the quantitative score for each particular level in the scale (Li) has to be determined. Basically, Li represents to what extend the implementation under evaluation complies with a given level i. Provided that the implementation fulfills the corresponding architectural requirements, the number of cognitive skills (CSi,j) present in the agent is taken into account. Even though the total number of cognitive skills considered for each level is different, the calculation of Li has to be pondered equally for all levels; in other words, Li is to provide a measure of the degree of accomplishment of level i, independently of the total number of cognitive features defined for each level. As mentioned in the definition of the scale, the first three levels (-1, 0, and 1) are of reference value, but they do not have any associated cognitive skills, therefore L-1, L0, and L1 are always 0 and there is no need to perform any calculation. For the rest of levels (2 to 11) the equation (1) is to be resolved. Equation 1:
Where ncsf (number of cognitive skills fulfilled) is the number of cognitive skills (CSi,j) that the agent entirely fulfills, J is the maximum number of cognitive skills considered for any level (10 in ConsScale V2), and Ji is the total number of cognitive skills defined in level i. Li is designed as an exponential curve in order to provide a meaningful value correlated with the existing synergy between the various cognitive skills that can be present at a certain level. Minimum possible value of Li is 0 and maximum value is 1. The latter means that level i is fully accomplished by the implementation. Once the value of Li has been calculated for each level, a Cumulative Level Score (CLS) can be obtained as indicated in equation (2). Equation 2:
CLS combines all particular level scores into a single measure that follows a logarithmic progression. The arrangement of the cumulative measure prevents the overall scale meaning to be distorted by the combined effect of poor Li scores in lower levels with high scores in higher levels. In other words, CLS enforces the quantitative measure to follow the same guideline as indicated in the qualitative measure. Finally, the CQS score is obtained evaluating the exponential function defined in equation (3). Equation 3:
Where K and a are constant numbers (0.97062765 and -1 respectively) specifically defined to normalize the score possible values from 0 to 1000. Consequently, the minimum score is 0 (which corresponds to ConsScale levels -1, 0, and 1) and maximum level of artificial consciousness is represented by a CQS of 1000 (for level 11). See [1] for more details about the CQS. Video CQS. Brief Description of ConsScale Quantitative Score (3 min.).
[1] Arrabales, R. Ledezma, A. and Sanchis, A. "Establishing a Roadmap and Metrics for Conscious Machines Development". In Proceedings of the 8th IEEE International Confenrence on Cognitive Informatics. G. Baciu, Y. Wang, Y.Y. Yao, W. Kinsner, K. Chan & L.A. Zadeh (Eds.). Hong Kong. June 2009. Pages 94-101. ISBN 978-1-4244-4642-1. |

This work is licenced under a Creative Commons Licence.


